Adis Ababa, 2 July (IANS). Malaria cases in Ethiopia are increasing rapidly. According to the World Health Organization, 5,20,782 malaria cases were reported in May. This is a large number recorded in a month.
The World Health Organization said in its recent report that apart from malaria in Ethiopia, outbreaks of other diseases like Kalra, Khasra and MPOX are also continuing. Due to the ongoing struggle in some parts of the country, access to health services has become difficult. People in these areas need immediate help. However, difficulties are coming up in providing assistance.
Malaria is a common disease in Ethiopia, especially in areas that are below 2,000 meters above sea level. The region covers three-fourths of the country, where about 69 percent of the population is in danger of malaria.
The outbreak of malaria usually increases between September to December and April to May, as these months come after rainy season. According to the WHO, in 2024, Ethiopia reported more than 84 million malaria cases, which is the largest figure in the country so far.
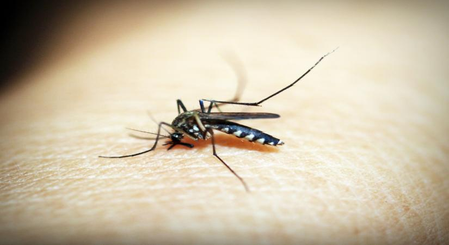
According to the health organization, malaria is a deadly disease, which is spread by the bite of certain types of mosquitoes. The disease is mostly found in countries where summer is very much. It is caused by a parasite and it does not spread from person to person.
Mild symptoms of malaria include fever, chills and headaches, while severe cases may cause fatigue, confusion, seizures, and shortness of breathing. Children, children under five years of age, pregnant women, passengers and HIV, AIDS people can be more affected by this disease.
It is necessary to avoid mosquito bites to prevent malaria. Mosquito nets and medicines can be used for this. If treatment starts at the right time, light cases can be prevented from becoming severe.
-IANS
MT/AS