New Delhi, 27 June (IANS). The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-BHU’s biomedical engineers have developed a special type of nano particles. These can prevent nanopartical blood clots from forming and can also treat thrombotic disorders (diseases caused by blood clots).
These low -cost nano particles can prove to be helpful in keeping blood in liquid state and increasing the efficiency of medical devices.
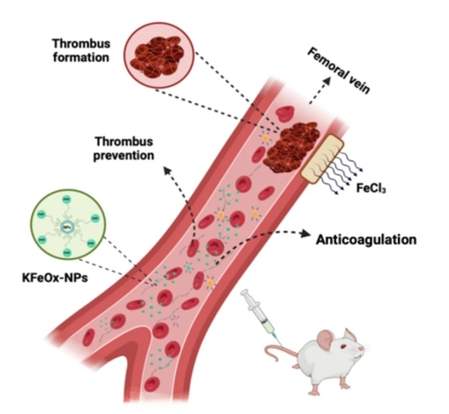
A team of scientists created Nano particles, called potassium ferric oxalate nano particles. They help prevent blood from freezing, which is called anticoagulation properties. This means that they can be helpful in keeping the blood thin, so that it flows easily in the blood vessels and does not interrupt.
Researcher Sudeep Mukherjee, a researcher at IIT-BHU School of Biomedical Engineering, said that these nano particles have been made from Potassium Ferric Oxlets. Potassium is essential for blood vessels and heart. Research found that these nano particles can keep the blood in a liquid state for 48 hours, which are important for safe collections, tests and transfusion of blood.
Researchers tested the safety and effectiveness of these nano particles in experiments conducted on mice. The results showed that these nano particles prevent clots in blood vessels and effectively control thrombosis (blood deposition) in mice. This was confirmed by ultrasound and power Doppler image. These nano particles prevent the formation of a protein called fibrin by connecting with calcium ions present in the blood, which helps in making blood clots.
Research also found that keeping the coat catheter (medical tube) in the blood from the particle stopped the clotting and reduced protein deposition, which improved blood flow.
The special thing is that these nano particles dissolve easily in water and do not accumulate in the body’s fat tissue, so that they are suitable for safe and biological applications.
Researchers say that these nano particles can help prevent long -term blood clotting and increase the efficiency of medical devices.
-IANS
MT/AS